Imagine you love working with PHP, a programming language primarily used to build websites (the backend that runs on a server). Before NativePHP, if you wanted to build an application that ran directly on a user’s computer (like Microsoft Word or Spotify), you’d have to learn an entirely new language like C++, Swift, or JavaScript frameworks.
NativePHP is a modern framework that changes this. It enables developers to use PHP and web technologies to build native-feeling applications for Windows, macOS, Linux, iOS, and Android. It integrates PHP with system APIs and modern runtimes, removing the need for platform-specific languages when creating desktop or mobile apps.
How Does It Work?
NativePHP is a tool that allows you to turn your PHP applications into standalone desktop apps. It takes your PHP code (often built with a popular PHP framework like Laravel) and bundles it with everything needed to run on a user’s computer, so there’s no need for them to install PHP or any other software.
It works in the following way:
- Your PHP Code: You write your application logic in PHP, just like you would for a website.
- The Runtime: NativePHP includes the PHP engine inside the app package, so the user doesn’t need to install PHP separately.
- The Shell: The app is wrapped in a native shell, a program that runs your application and displays its user interface.
- Native Access: NativePHP provides special tools called bridges that let your PHP code communicate with the operating system, enabling access to files, notifications, and other native features.
This bridge gives you access to things a web browser normally can’t touch, like:
- Showing native desktop notifications
- Managing application menus
- Accessing the user’s clipboard (copy/paste)
- Working with the local file system
Why use NativePHP ?
- Reuse Your Skills: If you’re a PHP developer, you can now build desktop and mobile apps without learning Swift, Kotlin, or other complex platform-specific languages.
- Cross-Platform: Write your code once, and with a few clicks, you can package it up to run on Windows, Mac, and Linux, and even iOS and Android.
- No Web Server Needed: Unlike a traditional web application, the app runs entirely on the user’s device—it’s fast and can work completely offline.
Hence, in the current tech world, if someone mentions NativePHP, they are almost certainly referring to the modern framework for building native desktop and mobile apps.
Differences Between Native PHP and Framework-Based PHP
When deciding how to build a PHP application, it’s important to understand the difference between Native PHP and Framework-Based PHP.
Native PHP involves writing code from scratch without relying on pre-built structures, giving full control but requiring more effort.
Framework-based PHP, on the other hand, uses frameworks like Laravel, Symfony, or CodeIgniter, which provide ready-made tools and a structured environment, making development faster and more secure.
The table below summarizes the key differences:
| Aspect | Native PHP | Framework-Based PHP |
| Definition | Writing PHP code directly without using a framework. | Using a PHP framework with pre-built libraries and structures |
| Development Speed | Slower as everything is coded manually. | Faster, with ready-to-use components like authentication, routing, and database handling. |
| Code Structure | Slower, everything is coded manually. | Standardized structure and coding conventions provided by the framework. |
| Security | Developers handle all security measures manually. | Built-in security features reduce risks of common vulnerabilities. |
| Learning Curve | Easier for beginners; focuses on core PHP | Requires understanding the framework’s conventions and tools. |
| Flexibility | Highly flexible; implement anything as desired. | Limited by framework design but ensures consistency and best practices. |
| Maintenance & Scalability | Can become complex and hard to maintain in large applications. | Easier to maintain and scale due to modular design and standardized patterns. |
Why Modern PHP is Still Highly Relevant
Modern PHP is relevant due to its Performance, Control, and Flexibility as they represent significant, measurable improvements in the PHP language itself, especially since the release of PHP 7 and 8.
1. Performance Advantages:
For a long time, PHP was seen as slow compared to languages like Node.js or Python. But this is no longer true.
JIT Compiler (PHP 8.x): The introduction of the Just-In-Time (JIT) Compiler in PHP 8.0 was revolutionary. Instead of interpreting the code line-by-line , JIT compiles the most frequently executed parts of the code into highly optimized machine code before execution.
What this means: For intensive tasks, like data processing, complex mathematical calculations, and running large-scale applications, the performance gains are massive. This allows PHP to handle millions of requests and massive user bases (like WordPress, Facebook, and Wikipedia which all heavily rely on PHP) with speed comparable to or even better than other modern languages.
2. Full Control Over Code
This advantage applies mostly to developers choosing to build an application with “raw” PHP (i.e., not relying on a full-stack framework like Laravel or Symfony) or, in the case of NativePHP, having a direct line of communication to the operating system.
In Web Development if a developer chooses to use Native PHP in the raw sense, they gain complete ownership over every single line of code. They don’t have to navigate a massive framework structure, which means:
-> No Unnecessary Abstraction: There are no layers of framework code slowing things down or obscuring how a feature works. The developer can write the most efficient, streamlined logic specifically tailored to their project’s needs.
-> Deep Optimization: It allows for granular performance tuning, letting the developer precisely optimize database queries, memory usage, and execution paths without fighting the constraints of a framework.
3. Flexibility and Zero-Overhead Development
This is where the modern NativePHP framework truly shines, bridging the gap between web development and native application development.
Maximum Flexibility: NativePHP allows a developer to use their existing PHP/Laravel web codebase and transform it into a desktop (Windows, Mac, Linux) or mobile (iOS, Android) application.
The Power of Reuse: Instead of hiring a separate team to build a Swift/Kotlin mobile app and a C# desktop app, a single PHP team can build and maintain all three (Web, Desktop, Mobile) from a single shared codebase. This is a huge cost and time saving for businesses.
4. Zero-Overhead Development
The zero-overhead here is primarily about the learning curve and tooling.
No New Languages: A PHP developer does not need to learn Swift, Kotlin, or a complex new JavaScript framework to create a fully installed desktop app. They continue to write their business logic in PHP.
Native Access with Ease: NativePHP handles the complex “bridge” between the PHP code and the operating system’s native features (like desktop notifications, system menus, file access, and clipboard control) using simple, clean PHP functions. The developer just calls a simple function, and the framework takes care of the hard, native part.
How PHP Works Behind the Scenes ?
The PHP Interpreter
PHP code is executed by the Zend Engine, which compiles PHP into bytecode and executes it efficiently.
The Request–Response Cycle
A user requests a page → PHP processes the request → interacts with the server → returns a response (HTML/JSON).
Role of the Web Server
PHP works with:
- Apache (most common)
- Nginx
- PHP built-in development server
Setting Up a Native PHP Environment
Installing PHP
You can install PHP on:
- Windows
- macOS
- Linux
Using XAMPP, MAMP, or WAMP
These bundles include Apache + PHP + MySQL, making it easy for beginners.
Using PHP Built-In Server
Run:

Folder Structure for Native Projects
A common structure is:

Core Syntax and Fundamentals
PHP Tags
PHP code starts with:

Variables, Constants, Data Types, Operators
PHP supports strings, integers, arrays, booleans, and objects. Operators include arithmetic, comparison, and logical operators.
Control Structures
if,else,elseifswitch- loops:
for,while,foreach
Functions in Native PHP
Built-In and User-Defined Functions
PHP contains hundreds of built-ins (strlen, array_merge, etc.) and allows you to create your own.
Anonymous Functions and Closures
Useful for callbacks and modular code.
Working With Forms and User Input
GET vs POST
- GET: visible in URL, used for reading data
- POST: used for submitting sensitive data
Sanitizing and Validating Data
Always sanitize user input using:

Native PHP and Databases
Using MySQL or MariaDB
The most common database for PHP apps.
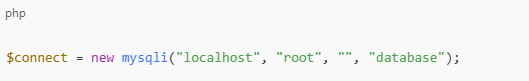
Connecting Using MySQLi
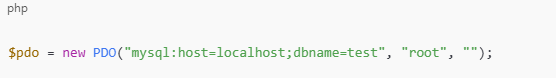
PDO (Recommended)
Supports prepared statements and multiple databases:
CRUD Operations
You manually create logic for:
- Create
- Read
- Update
- Delete
Preventing SQL Injection
Always use prepared statements.
File Handling in Native PHP
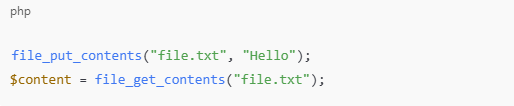
Reading and Writing
Uploading Files
Use $_FILES and validate file types.
Working with Directories
mkdir, scandir, and rmdir help manage folders.
Sessions, Cookies, and Authentication
How PHP Manages Sessions
Sessions store user info temporarily on the server.
Building Login Systems
Native PHP lets you create your own:
- login forms
- session handlers
- authentication classes
Security Best Practices
- Use password hashing
- Validate all inputs
- Implement CSRF tokens
Object-Oriented Programming (OOP) in Native PHP
PHP is a full object-oriented language supporting:
- Classes and objects
- Inheritance
- Interfaces
- Traits
- Polymorphism
Namespaces and Autoloading
Use Composer’s autoloader for modern project structuring.
Advanced Native PHP Concepts
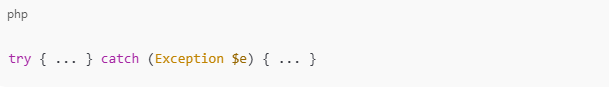
Error Handling and Exceptions
Use:
Working with APIs
Native PHP can consume or create APIs using :
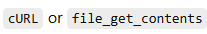
JSON and XML
PHP supports both formats natively.
PHP 8+ Features
- JIT compiler
- Attributes
- Union types
- Match expression
Security in Native PHP
Major Threats
- XSS
- CSRF
- SQL Injection
Password Hashing
Use:

Secure Sessions
Regenerate session IDs and store minimal data.
Performance Optimization
Caching
Use output buffering or full-page caching.
Opcode Cache
Enable OPcache for significant performance boosts.
Reducing Server Load
Optimize loops, avoid unnecessary queries.
Optimize SQL
Use indexing and prepared statements.
Real-World Native PHP Projects
1. Simple Content Management System (CMS)
Manage pages, posts, and categories without a framework.
2. Contact Form System
Process and send emails with validation and security.
3. API-Based App
Build lightweight REST APIs using pure PHP.
Future of Native PHP
Native PHP has evolved significantly over the years, especially with the release of PHP 8, 8.1, 8.2, and 8.3. These versions brought features such as the JIT compiler, attributes, union types, named arguments, readonly properties, and major performance improvements. Together, these updates have transformed PHP from a simple scripting language into a highly efficient, modern, and secure backend technology.
Faster and More Efficient Than Ever
PHP 8’s JIT (Just-In-Time) compiler dramatically boosts execution speed in CPU-intensive tasks. Combined with OPcache improvements, PHP scripts execute faster with fewer resources. This makes Native PHP applications extremely lean, responsive, and cost-efficient — especially on low-memory servers or shared hosting.
Modern Syntax and Developer-Friendly Features
Native PHP now supports strong typing, improved OOP features, error handling, and more predictable behavior. This modern syntax makes PHP code cleaner, more readable, and easier to maintain. Developers can build structured, scalable applications even without frameworks, thanks to these native enhancements.
Why NativePHP Still Has a Strong Future Ahead
Even as frameworks become more common, NativePHP still holds a permanent and important role in the development world.
1. Great for Learning
Building applications in NativePHP teaches you how the language really works:
- How requests are handled
- How routing is built
- How sessions and cookies function
- How to structure files and utilities
This foundational knowledge makes learning advanced frameworks like Laravel much easier. Developers who start with Native PHP become stronger, more confident programmers.
2. Ideal for Small Tools and Lightweight Applications
Native PHP is perfect for building:
- Simple admin dashboards
- Utility scripts
- Contact forms
- Data processors
- Small CRUD apps
- Automation tasks
These projects don’t need a heavy framework. Native PHP keeps them lightweight, fast, and easy to deploy.
3. Perfect for Systems That Require Maximum Performance
Frameworks add layers of abstraction that slow things down. In contrast, Native PHP gives you:
- Direct access to the language
- Zero overhead
- Faster execution
- Minimal server load
This makes it an excellent choice for performance-critical applications, microservices, and APIs where speed matters more than built-in features.
4. Easier to Deploy on Shared Hosting
Most shared hosting providers support:
- Native PHP
- MySQL
- cPanel or similar tools
But they do not support:
- Composer-based deployments
- Framework-specific requirements
- Complex directory structures
Native PHP apps can be uploaded and run immediately, making them ideal for freelancers, small businesses, and low-budget projects.
Native PHP Isn’t Going Anywhere
Despite the popularity of frameworks, Native PHP remains the core foundation of PHP development. Every framework – Laravel, Symfony, CodeIgniter – ultimately runs on top of Native PHP. This means:
- Understanding Native PHP improves your framework skills.
- You can fix problems more easily.
- You can build custom features when frameworks fall short.
As PHP continues to evolve, Native PHP becomes even stronger, faster, and more versatile. Whether you’re building small tools or optimizing high-performance systems, Native PHP remains a reliable and essential skill for any developer.
Conclusion
Native PHP is a timeless, flexible, and powerful approach to web development. Whether you’re a beginner learning how PHP works or a developer creating a lightweight, high-performance app, understanding Native PHP gives you the fundamentals that frameworks are built on. Learning Native PHP helps you become a better, more complete, and more confident developer.
If you’re looking to build or modernize a PHP-based application, our team at Zasya Solutions can help you craft scalable, secure, and high-performance solutions.
Reach out to us today to discuss your project or request a consultation!